| Nov 4, 2023
SEO for Manufacturers and Industrial Companies: The Ultimate Guide for Securing Page One Rankings
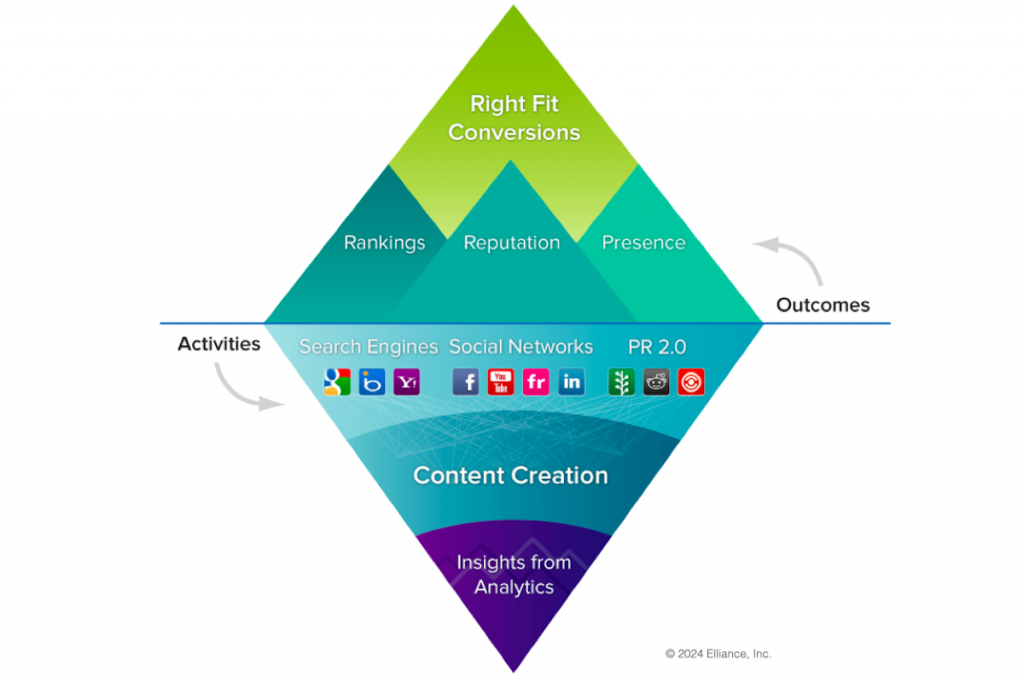
Investing in SEO for manufacturers and industrial companies generates more qualified leads, opens new markets and liberates new revenue. This guide was written to help the manufacturers and industrial companies with modest marketing budgets to leverage SEO to out-smart and out-compete the deep pocketed Goliaths without outspending them. We call them small giants. To paraphrase Guy Kawasaki, if you have more money than brains, you should focus on paid advertising, but if you have more brains than money, you should focus on SEO marketing. As one of the leading manufacturing marketing agencies, we learned the strategies and tactics presented here from serving numerous manufacturers who were small giants in their respective categories. We thrive on seeing them prosper and we celebrate their success.
Table of Contents:
I. SEO Basics for Manufacturers
- What is SEO?
- What are SEO Ranking Factors?
- What is Inbound Marketing?
- Know That SEO/Inbound/Content is a Long Game
II. Eight Reasons Why Manufacturing and Industrial Marketers Are Deploying SEO
III. The 3 R’s of Manufacturing Prosperity
- Revenue
- Reputation
- Rankings
IV. Ten Elements of an SEO Audit
V. Formulating a Keyword Strategy for Industrial Companies
- Shape Your SEO Strategy
- Conduct Keyword Research
- Create Fresh Inbound Content Strategy
VI. SEO Implementation Guidelines and Tips for Manufacturing Companies
- Implement On-Page Factors
- Make Your Website Responsive, Secure and Fast
- Build Quality Inbound Links
- Manage Social Signals
- Optimize for Locations and Geographies
- Create Fresh Content to Secure and Sustain Top Rankings for Important Keywords
VII. Monitoring of Keywords and SEO Performance for Manufacturers
VIII. Adapt to Changes in SEO Algorithms
I. SEO Basics for Manufacturers
What is SEO?
SEO or “search engine optimization” is the process of improving your website rankings and visibility on Google, Bing and other international search engines.
Manufacturers that pursue and achieve top organic or natural Google and Bing rankings prosper and thrive. There is a good reason for this. Organic rankings are more trusted, more clicked and out-convert paid advertising leads three-fold. The best prospective buyers prefer to “discover” the manufacturers of their choice through “accidental finds” on Google and Bing page one and via word-of-mouth on social media and influencers.
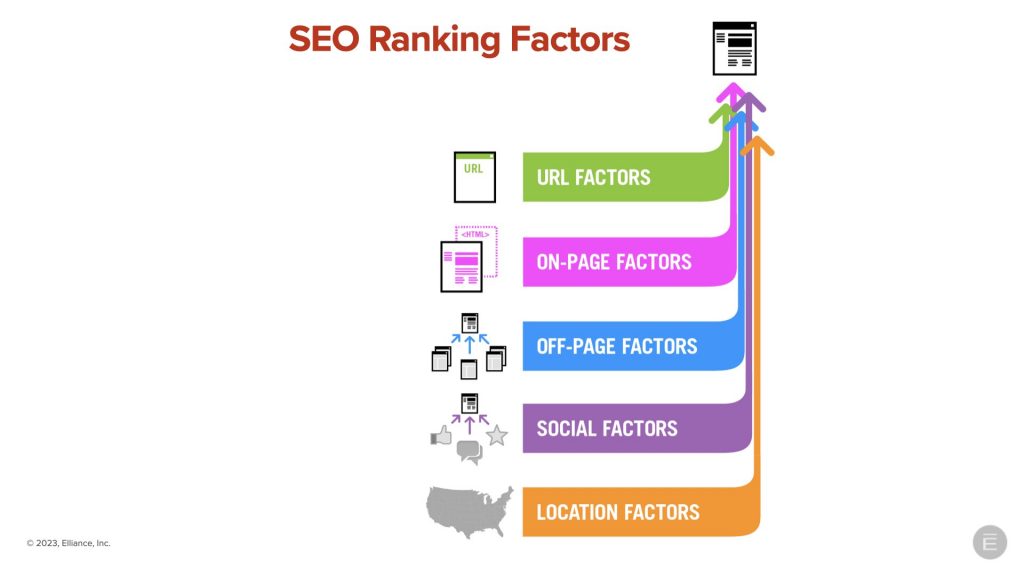
What are SEO Ranking Factors?
Five factors affect search engine rankings:
- URL factors: Use symbolic and phrase tokens, not numbers. Use international domains for country-specific content.
- on-page factors: Use meta-data and infuse keywords into copy.
- off-page factors: Secure inbound links from reputable websites to your website.
- social factors: Foster conversations and content sharing on social media.
- local factors: Embed location and country signals for your target regions.
What is Inbound Marketing?
Because rankings weaken over time and search engines reward fresh content, marketers must create a continuous stream of high quality, trusted and relevant content (such as articles, blog posts, videos, infographics, white papers, thought leadership articles, social posts, quizzes, games, etc.) and ignite it via promotion and conversation-starters to encourage peer-to-peer sharing. Thus the label SEO has evolved into SEO/Inbound/Content marketing.
Inbound marketing creates a hub of value and trust. As this foundation is established, the cost to build upon it naturally drops. This means a very strong ROI over time for an inbound marketing focused approach.
Metaphorically speaking, an inbound marketing strategy is simply the act of gathering combustible firewood and igniting it.
Know That SEO/Inbound/Content is a Long Game
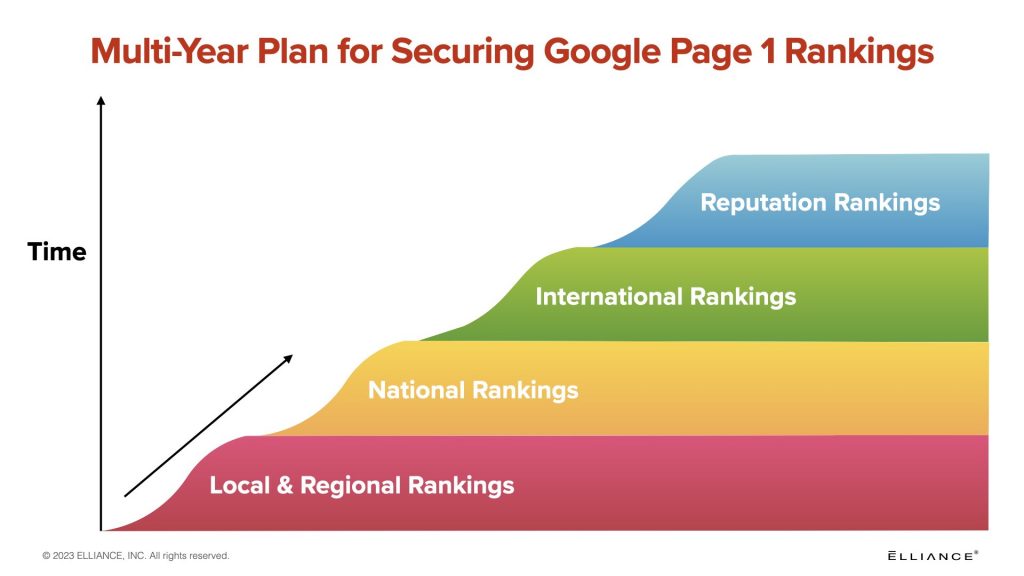
It takes several months to achieve local and regional rankings, and a year or more to achieve national and international rankings. Manufacturing marketers who have the patience and determination to achieve Google rankings create an enduring, rising tide of rankings and are able to reduce their paid marketing spend as SEO rankings are achieved.
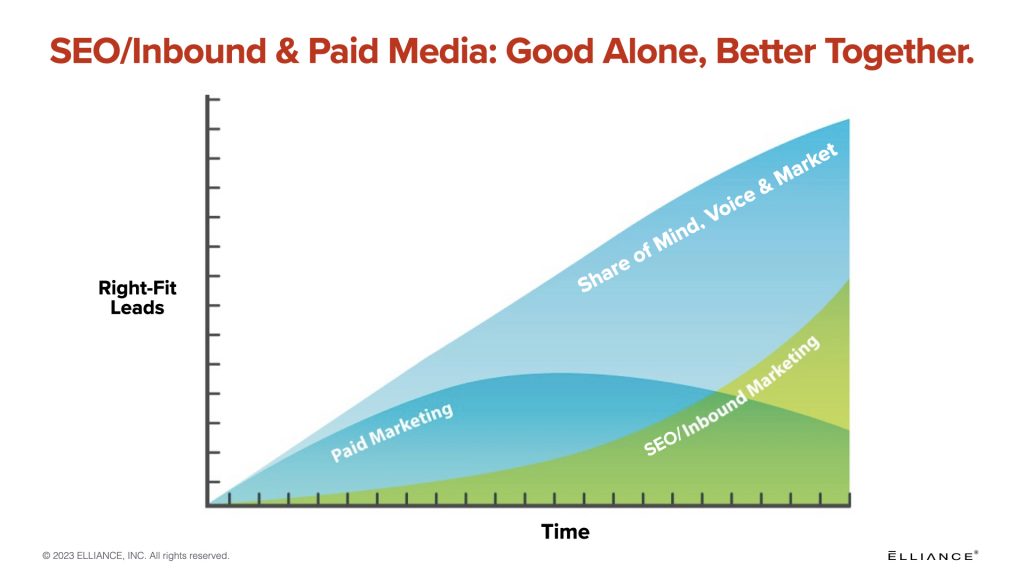
Paid advertising and SEO/Inbound/Content marketing are good alone, better together.
II. Eight Reasons Why Manufacturing and Industrial Marketers are Deploying SEO
In serving more than one hundred manufacturers in our thirty year history, we have helped our clients overcome the following eight business challenges with SEO.
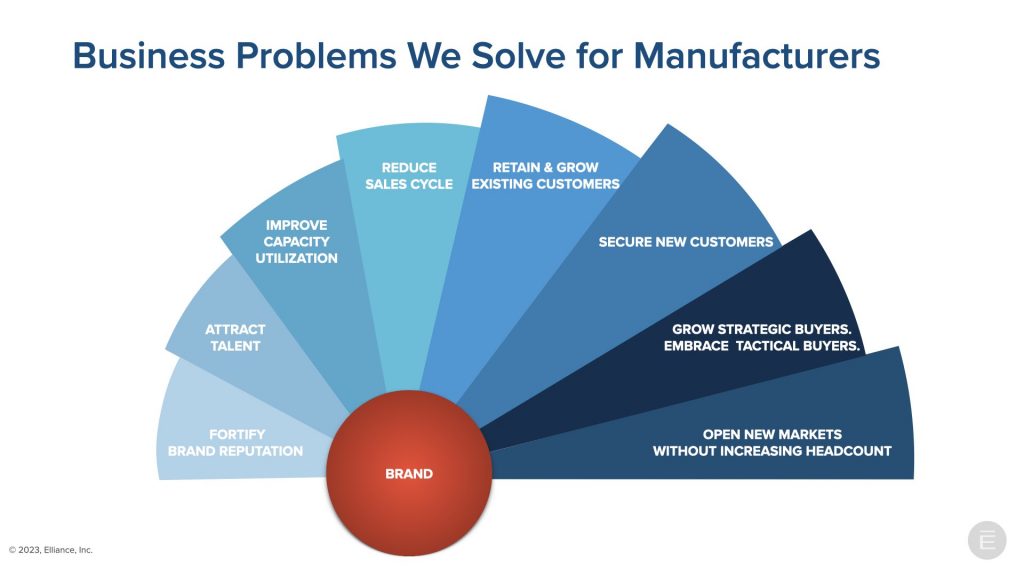
Fortifying Brand Reputation
Branding allows manufacturers to charge a premium and for financial markets to value them higher. Smart manufacturers infuse the brand in every touch point and optimize each digital asset for Google rankings. They project thought-leadership and communicate their environmental, social and governance (ESG) standards and corporate social responsibility (CSR) credentials.
Attracting and Retaining Talent
All manufacturers are challenged by a national talent shortage to fill the new jobs they’re creating. Instead of relying on tired, old ways, smart manufacturing marketers are engaged in Recruitment 3.0 which demands a better digital strategy that grabs the attention of the most talented people out there. One that doesn’t commoditize businesses by constantly putting them side by side with everybody else looking to fill seemingly look-alike roles. One that articulates and celebrates the company’s values to match the needs of values-based Gen-Z and Millennials. One that SEO-optimizes each job in the careers and job listing pages so it can surface on Google page one.
Improving Capacity Utilization
Capacity utilization is one of the underpinnings of manufacturers that is maximized with predictable demand generation. SEO liberates new business better than any other marketing tactic.
Reducing Sales Cycle
Even though manufacturers know that their buyers make decisions based on their budgetary cycles, they invest in streamlining and trimming the buying cycle by educating tactical buyers and reassuring prospective buyers with thought leadership content.
Retaining, Growing and Cross-Selling to Existing Customers
Because it takes up to five times more resources to acquire a new customer than to retain an existing one, successful manufacturers project thought leadership and confirmation to buyers of past purchase decisions.
Securing New Customers
By dominating national and international search engines and social media, manufacturers secure:
- new customers from global markets
- new customers who are not aware of the company
- new customers seeking second source suppliers
- new customers disappointed by a bad experience with competitive suppliers
Growing Strategic Buyers. Embracing Tactical Buyers.
Manufacturers attract and convert high-margin strategic buyers with thought leadership content; in tandem, they convert tactical and transitional buyers with educational content.
Opening New Markets without Increasing Headcount
Smart manufacturers open new markets by securing top search engine rankings, growing their international presence in global markets, and being discovered by strategic partners in new markets.
In short, Google/Bing page one rankings are the best means for finding, getting, keeping and growing customers and talent.
III. The 3 R’s of Manufacturing Prosperity: Revenue, Reputation and Rankings
The primary goal of manufacturing marketing is to grow rankings, reputation and revenue for manufacturers. Even though most manufacturers are investing between 2% to 5% of their revenue on marketing, the most aggressive manufacturers are investing close to 10% of their revenue on marketing. Of course not all of the marketing budget is allocated for SEO marketing, but between 30% to 50% goes towards this all-important tactic.
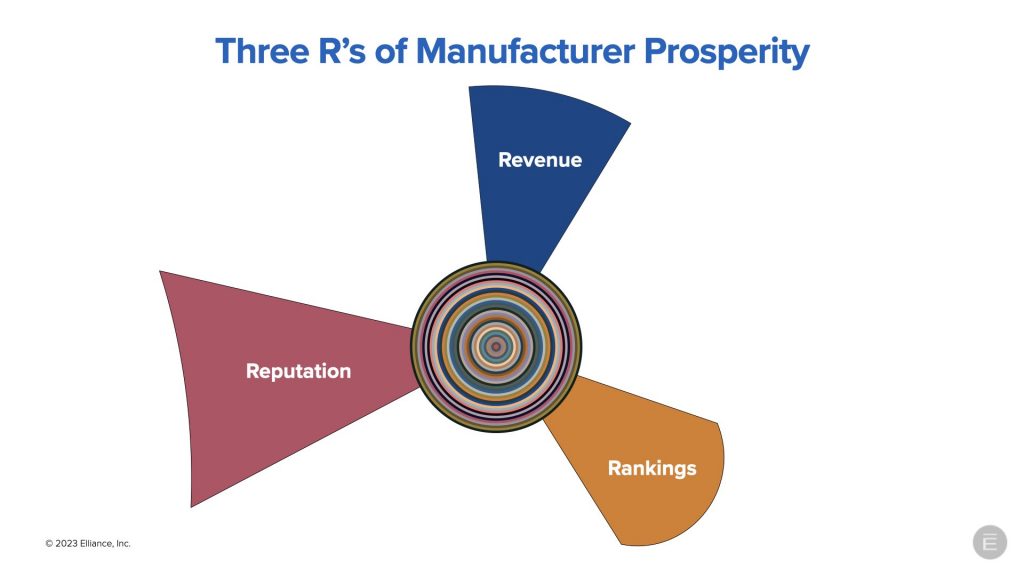
1. Revenue
Amongst manufacturers, revenue can flow from three primary sources: direct sales; distributor, resellers and agent sales; and OEM’s. Revenue can also come from various market segments.
SEO marketers deploy a unique set of strategies to liberate sales from one or more of these channels and segments. While the existing products generate a lion share of revenue, new products are launched and routinely added into the product mix.
2. Reputation
All great manufacturing marketers engage in branding to position their companies as suppliers of consequence. They curate, orchestrate and elevate their content strategy to deftly manage their corporate destiny with stories, case studies, videos and infographics on websites and social media channels. They maximize their content productivity and amplify their thought leadership with SEO Keyword Lexicons and best search engine optimization practices. They widen their content reach beyond their customers to new customers and influencers. They carefully manage their reputation within the communities they operate in.
3. Rankings
Successful manufacturers understand that they must influence the twin third party and Google (plus Bing and more) rankings. They understand the factors that weigh into each ranking and proactively influence those factors with talented team members and agency partners.
IV. Ten Elements of an SEO Audit
To begin the SEO journey, smart manufacturers conduct an SEO audit to assess the following:
1. Website Performance Metrics Audit
Begin by testing site load speed, mobile/desktop performance, secure certificate and domain name analysis. These are all Google and Bing ranking factors.
2. Website URL Structure Audit
Ensure it is rational, descriptive and hierarchical. A good URL structure will accelerate attainment of stronger rankings and simplify analysis of website performance in Google analytics.
For international search rankings, ensure country-specific domains are being leveraged.
3. Website Copy and Content Audit
Optimizing website copy and incorporating relevant keywords is a fundamental aspect of successful SEO for manufacturers. The website copy must persuade prospective buyers, reassure current customers and inform/influence Google and Bing bots. It must also be infused with appropriate keywords and keyword derivatives.
For international search rankings, ensure translated copy exists in country-specific languages.
4. Keyword Audit
Evaluate keywords on all website pages. Detect keyword stuffing, an illicit SEO technique in which keywords are loaded into a web page’s meta tags, visible content, or link anchor text in an attempt to gain an unfair ranking advantage. At best, search engines disregard them and, at worst, penalize a website if it’s packed with too much, irrelevant or unrelated content.
5. User Experience Audit
Google and Bing bots reward websites with superior user experience, information architecture and page architecture – for buyers and channel partners alike. Evaluate it carefully.
6. Conversion Architecture Audit
If a website is a manufacturer’s #1 salesperson, it must be efficiently constructed to maximize lead and e-commerce order generation, signing up for newsletters and webinars, accessing thought-leadership content behind registration walls. And if the website is a manufacturer’s service extension, it must efficiently steer customers to after-sales service and knowledge base portals. It must also serve all channel partners with efficiency and grace.
7. SEO Coding Audit
Websites are built with HTML and CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) which are instructions to browsers to determine characteristics of web page elements such as text size, position of elements on the page, etc. Furthermore, ADA WCAG 2.1 standards dictate accessibility compliance for various audiences. Websites must be constructed with best practices because Google and Bing both reward them and penalize websites that don’t.
8. Social Signals Audit
Presence of social sharing buttons and open-graph (OG) tags facilitate content sharing which is a Google, Bing and international ranking factor. Ensure they are present.
9. Internal and External Links Audit
While it’s true that internal site-links and in-bound links are the backbone of Google’s ranking algorithm, outbound links also play an important role. Ensure only highest quality links exist and itemize poor quality links for subsequent link-pruning.
10. Blog Audit
Blogs are one of the most effective means of securing and lifting Google and Bing page one rankings. An audit of its categories, tags and content audit will reveal areas of improvement.
Armed with the audit, the industrial marketer is ready to do the hard work of crafting a keyword strategy.
V. Formulating a Keyword Strategy for Industrial Companies
First, shape your SEO strategy around your goals
Implementing effective SEO for industrial companies requires a solid keyword strategy has at least three elements:
- The right mix of keywords focused on revenue, reputation and thought leadership goals. Begin by choosing the right set of keywords from the get-go.
- The right situational analysis of your competitor keywords and their rankings. Know who’s sleeping, who’s awake, who’s ahead, who’s behind, and who’s the 800 pound gorilla.
- The right time horizon to achieve local, regional, national and international rankings. Develop a plan that goes after the lowest hanging fruit first (local and regional rankings), then harder-to-achieve national rankings, and finally the hardest-to-achieve international and reputation rankings. Slow and steady wins the race.
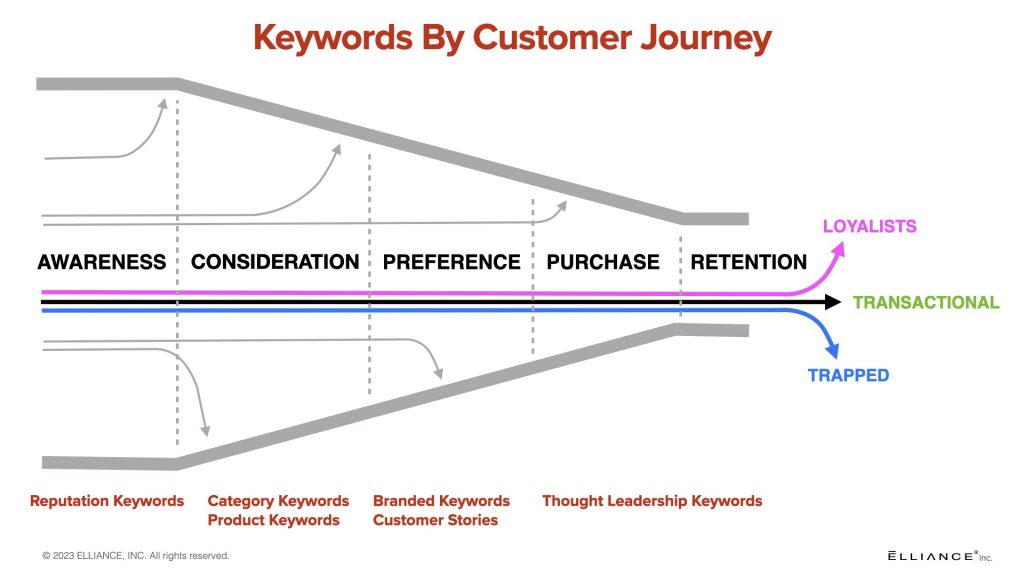
- The right keywords that span the entire decision funnel. Know that prospects use different clusters of keywords at each phase of the decision funnel. e.g. they’ll use reputation keywords during the awareness phase, category keywords during the consideration phase and branded keywords during the preference/purchase phase and thought-leadership keywords during the purchase decision phase.
Next, conduct keyword research
Industrial companies use third party keyword tools, comb paid advertising data, audit content archives, mine sales history data, and review market research data to develop a Keyword Guide.
When optimizing for highly-competitive terms, strategically clustering related phrases around the main keyword can cause a halo effect in the SERPs. Remember to incorporate keyword clusters. For example, for a pioneering logistics management company that wished to “own” the phrase “logistics” in addition to “logistics software”, we created several hives of keywords using a clustering strategy:
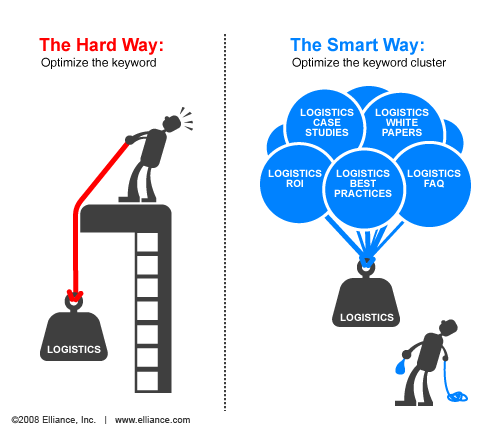
For their software division, claiming rankings for “logistics management software” keywords required the use of long-tail keyword strategy. We’ve discovered that buyers drill down from lower-converting, short, general keywords to longer, 3- or 4-word phrases that are more likely to convert a prospective buyer.
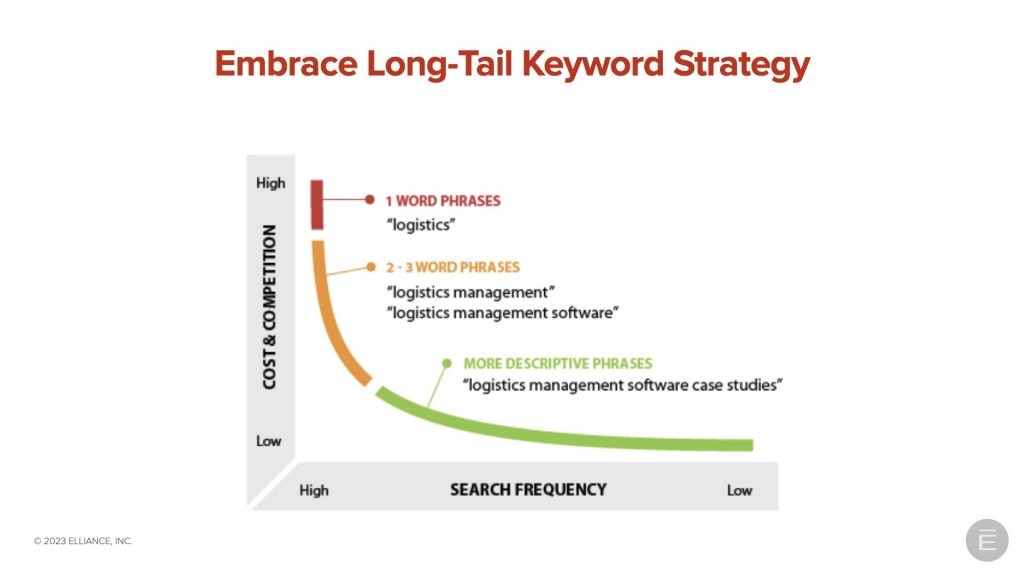
When preparing a keyword guide, ensure you include both long-tail keywords and high-traffic phrases.
Since searcher behavior has evolved from keyword era, to keyword cluster era, to natural language era and has now entered the epoch of voice search, ensure that keyword clusters, frequently asked questions, colloquialisms and “near me” keywords are all represented in your keyword selection.
Finalize the Keyword Guide into the following buckets:
- Product Keywords
- Brand Keywords
- Geographic Keywords
- Decisioning Keywords
- Reputation Keywords

Map some of your keywords to unique pages of your website map.
Now you need to develop a plan for international content and future content.
Then create content for countries of Interest
Build language-specific or country-specific microsites to target prospects from specific countries. Build microsites for large countries (e.g. China), and build language-specific websites for country clusters (Latin America).
Apply SEO best practices to the country-specific microsites for country-customized Google and Bing search engines – as well as country-specific search engines such as Baidu for Chinese, Yandex for Russia, etc.
Lastly, create a fresh inbound content strategy
Because Google’s algorithm rewards fresh content, creating high-fidelity fresh content is the third crucial leg of inbound/content marketers that helps manufacturers “get found” via search engines, word-of-mouth and the sharing of content. Inbound marketing involves the continuous creation of relevant and high quality content, such as PR2.0 assets, articles, social posts, blog posts, videos, infographics, white papers and thought leadership events, and igniting that content through promotion and conversation-starters to encourage peer-to-peer sharing.
Carefully curated content is distributed through channels you control (your “owned” media, such as your website and social networks) and the channels you don’t control (the social media of people/organizations in your network), where our content strategists spark conversations on your behalf. Carefully managing the content you own allows you to influence the content you “earn” and reputation you build. Search engine rankings and social connections (“likes,” “shares,” etc.) are among the most trusted endorsements online today. Managing your content and your interactions carefully allows you to maximize your success in SEO and the social world. Finally, advanced analytic approaches allow you to improve your understanding of the content and communications your prospects value.
Create an editorial calendar for fresh inbound content with the following buckets:
- Education content for tactical buyers
- Thought leadership content for strategic buyers
- Story or cause-related content for building brand reputation
- Newsjacking content to tie the brand with current issues
VI. SEO Implementation Guidelines and Tips for Manufacturing Companies
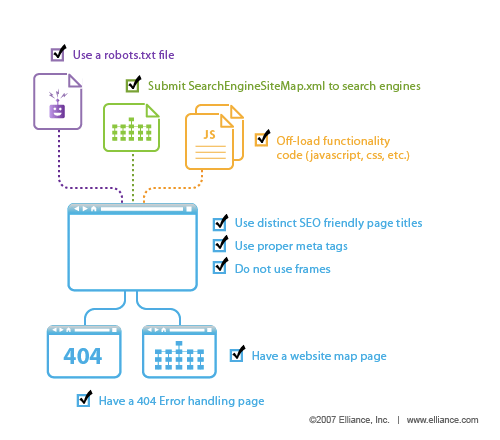
1. Implement on-page and on-site factors
When it comes to SEO, there are certain elements that need to be in place for all manufacturing websites. Are your 301 redirects in place? Is the robots.txt file authored to allow adequate crawling? Is your XML sitemap ready for search engine crawlers? This infographic depicts a handy checklist that will help get you through any implementation of SEO for manufacturing companies.
2. Make Your Website Responsive, Secure and Fast
Google, Bing and international search engines reward responsive websites – ones that auto-adjust gracefully on smartphones, tablets or desktops. Google also ranks websites higher that load fast and are running in secure mode.

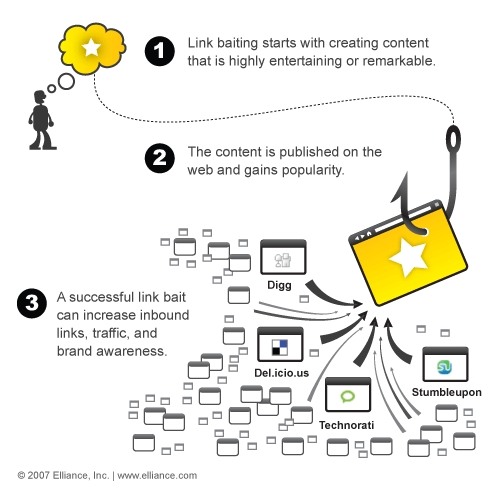
3. Build quality site links
Link Baiting is used to get many quality inbound links pointed to your site. Through great content or some humorous hooks, create a viral marketing effect using this technique.
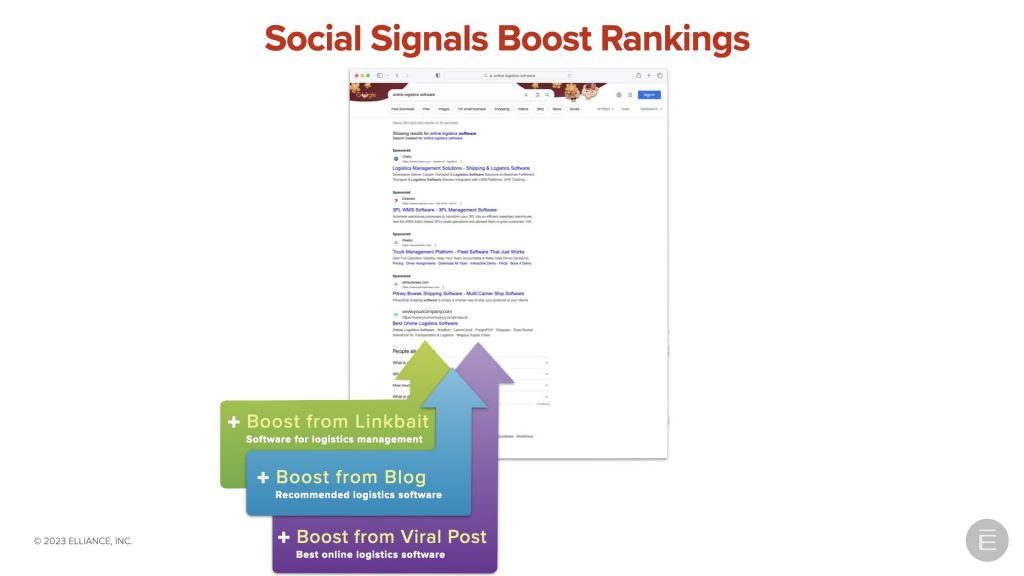
4. Manage social signals
Google, Bing and international search engine bots eavesdrop on social conversations to rank their sites. Creating share-worthy content and enabling sharing so it gets passed around is a sure way to improve your search engine rankings.
5. Optimize for locations and geographies
The geo-targeting search strategy you decide to use will impact your overall SEO campaign. Embedding location signals into your website and content will help rank it in those geographies.
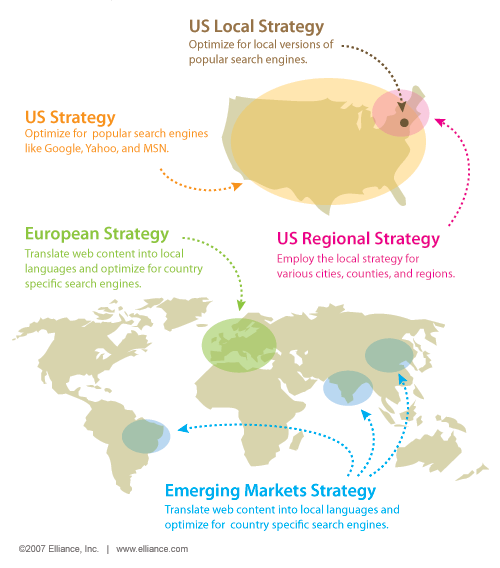
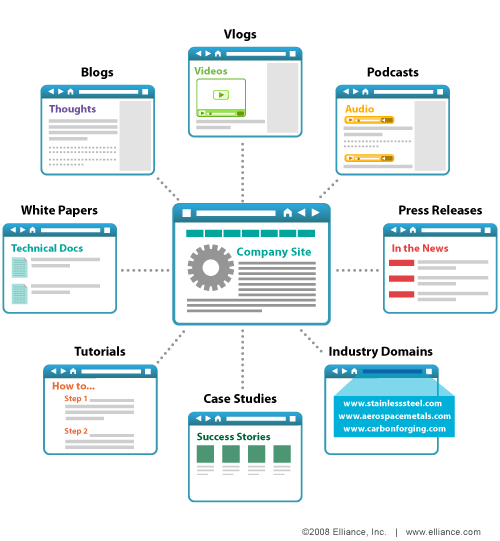
6. Create Fresh Content to Secure and Sustain Top Rankings for Important Keywords
Since Google, Bing and international search engines reward websites with fresh content, develop a content strategy to create buckets of new content (microsites, blogs, magazines, etc.) for various parts of the sales funnel. Inform all content with the Keyword Lexicon.
Create and publish unique content as follows:
- Understand prospective buyers and buyer behavior
- Interview subject matter experts (SME’s) and industry experts to create thought leadership content and white papers
- Conduct original research with fresh insights to secure your position as an industry leader
- Interview process team members to create educational and how-to content for various use cases
- Interview loyal customers to create customer interviews and case studies
- Create premium content tailored for specific customer segments
Fresh content may take several forms.
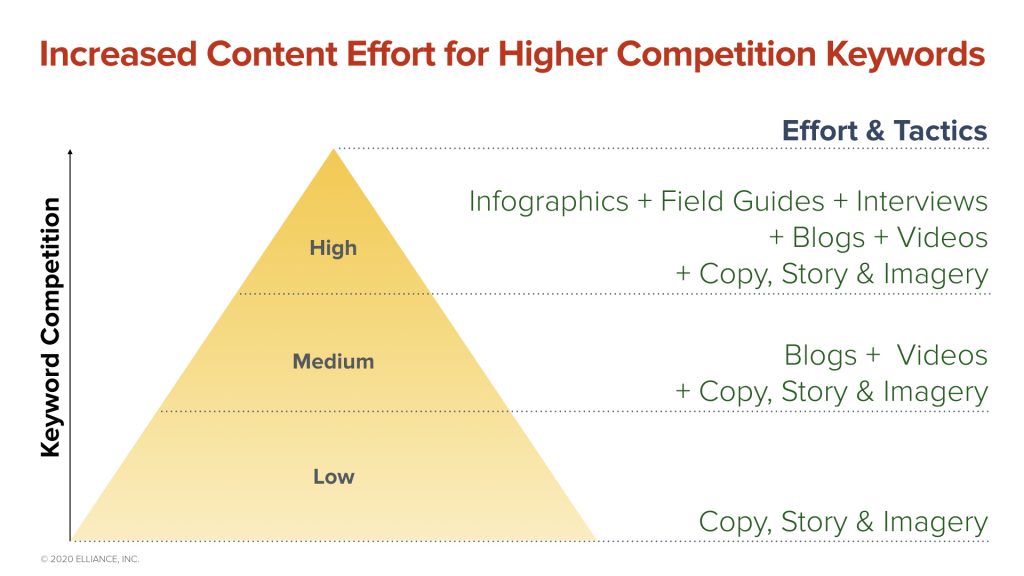
The more competitive a keyword, the more high-fidelity content (infographics, videos, quizzes, etc.) you’ll have to create to secure and sustain page 1 rankings.
VII. Monitoring of Keywords and SEO Performance for Manufacturers
To quantify the return-on-investment, manufacturers must connect the dots between SEO efforts and conversions. Activate Google Analytics and Google Search Console. Integrate marketing automation software like HubSpot or Pardot in your website, blog and content channels.
Some of the SEO metrics that manufacturers must continuously measure are:
- Brand impressions
- Traffic/Organic traffic including quality, sources, locations and devices
- Keyword rankings
- Branded vs. non-branded keywords
- Page popularity
- Leads, sales and customer service requests that originated from search engines
Measure keyword rankings and monitor competitors periodically. Respond to encroachment with counter-moves on an as-needed basis.
VIII. Adapt to Changes in SEO Algorithms
Industrial marketers must realize that getting on page 1 is not a one-and-done game. Since Google, Bing and international search engine algorithms change periodically, the strategies for securing page 1 positions must be adapted regularly.
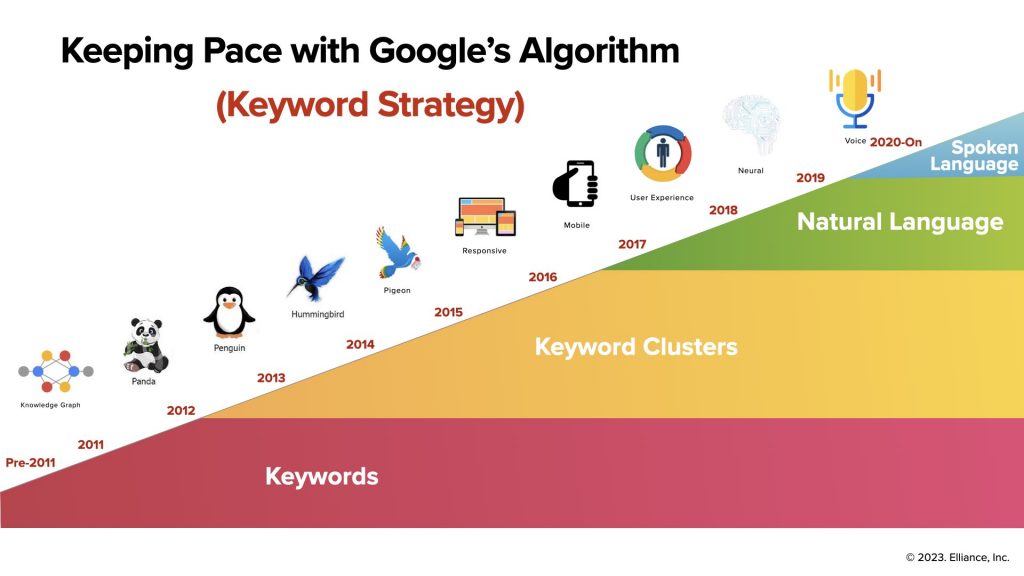
For instance, to give you a sense of the big changes in Google’s algorithm and the ranking factors in the last decade, we have created a simplified chart below:
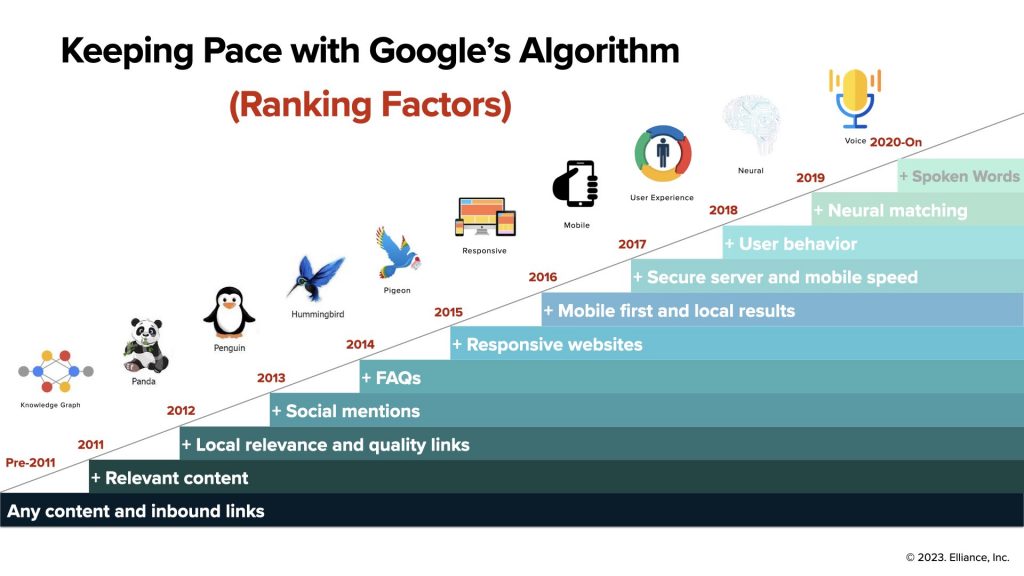
The search terms people type in the Google search box have changed dramatically too, and can be understood in four distinct epochs: the keyword era, keyword cluster era, natural language era and now the voice era. Voice activated searches now account for more than half of all searches. Manufacturing marketers must ensure that keyword clusters, frequently asked questions, colloquialisms and “near me” keywords are all represented in their keyword selection.
I hope you found this guide helpful. If you are an industrial marketer, contact us if you are seeking a high performance SEO agency or a smart manufacturing marketing agency which can help you join the elite group of manufacturers growing their company’s share of mind, voice and market.
